RNAseq of experimentally evolved plants to male and female traits
Lines with large and small flowers (good for females and males, respecively) have been generated by artificial selection. Gene expression differences between those lines should reveal the first genes that respond to such sexually antagonistic selection.
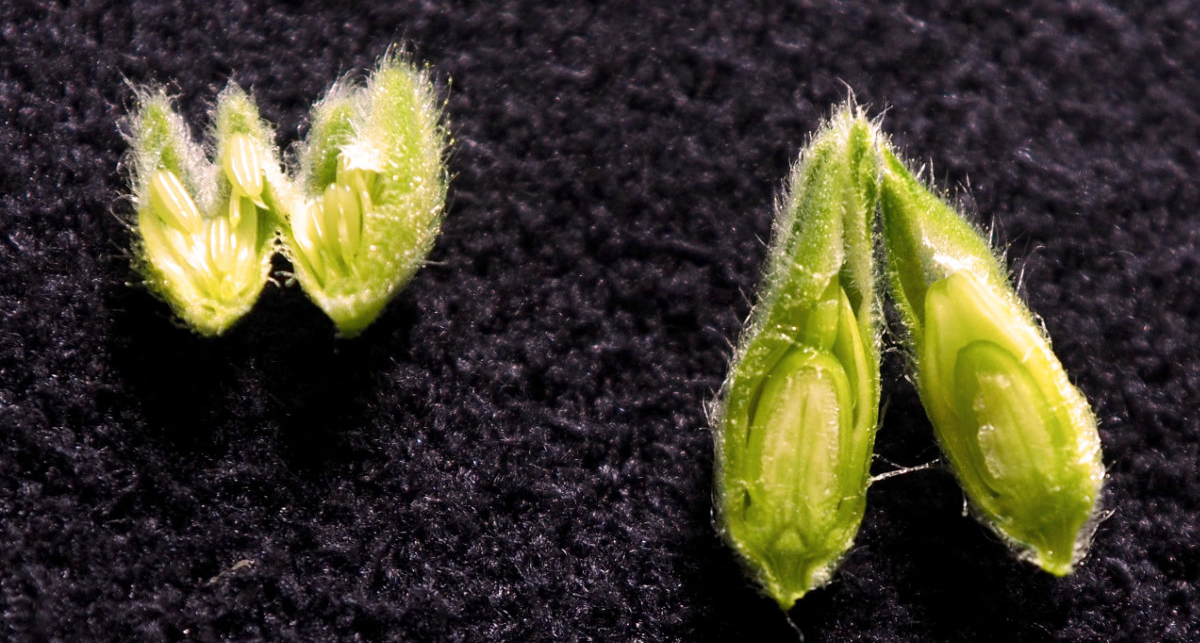

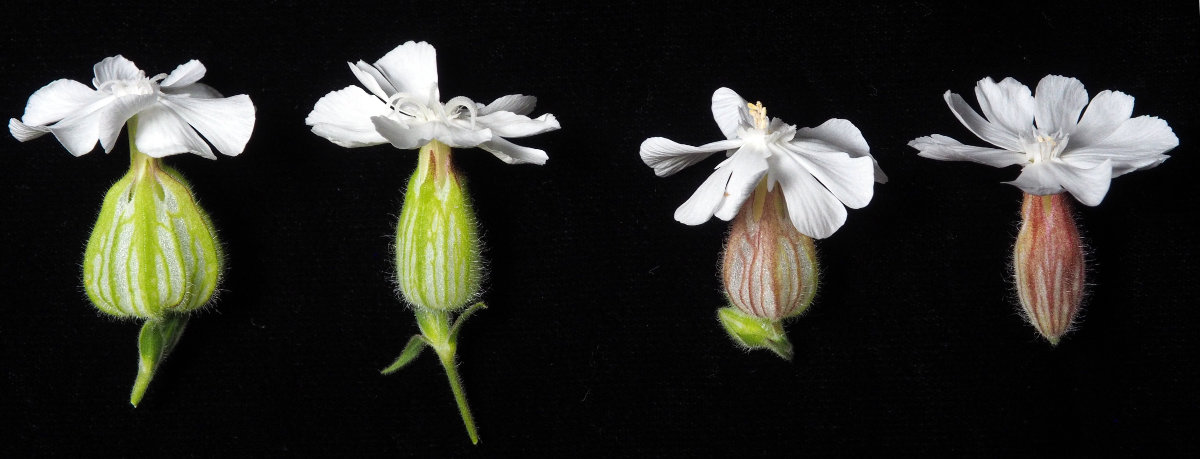
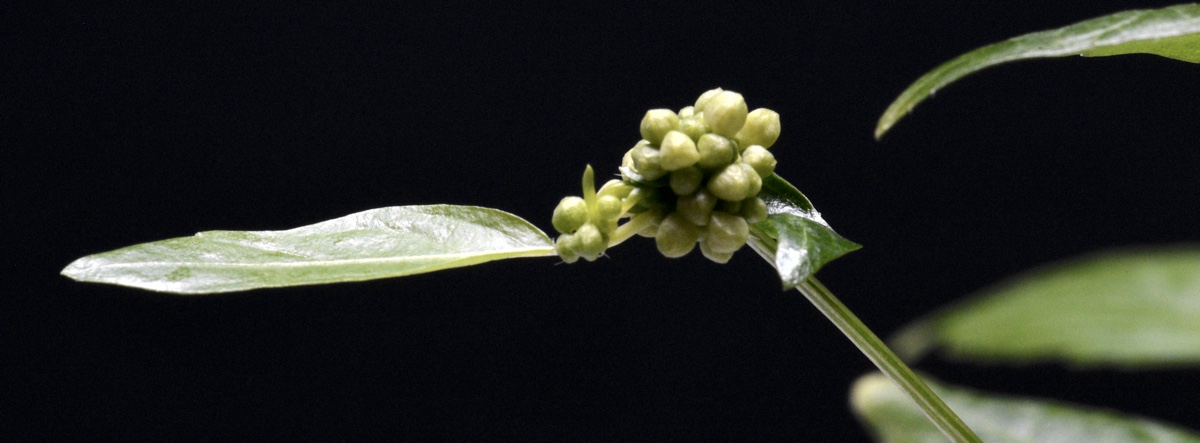
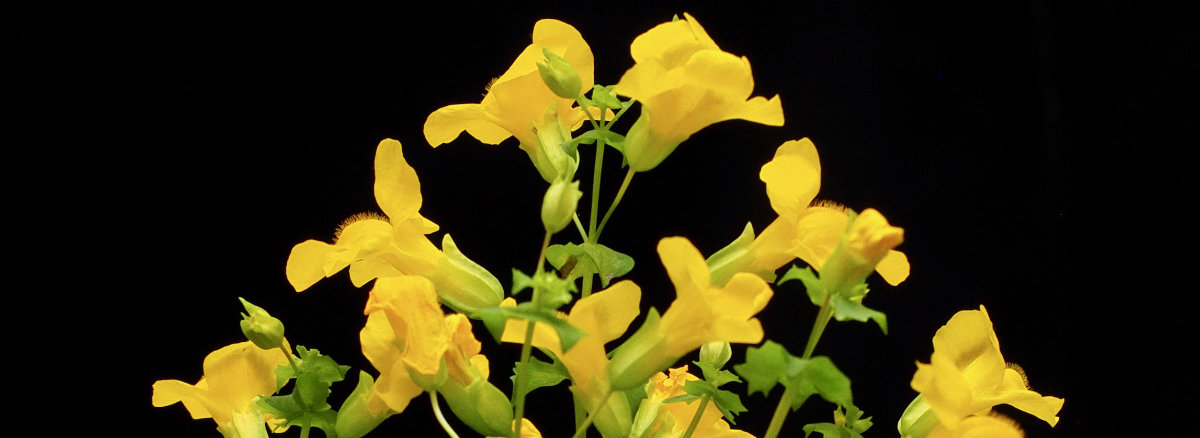
Example of the developmental status of flower buds used for RNA extraction.
Plants from the same population have been selected for 4 generations on flower size. Both large and small flower size lines have been generated.
Flower size has different optima yet differs between the sexes, with large flowers being beneficial to females. We are investigating the changes in gene expression associated with selection in one sex at a time.
We are particularly interested in the genomic location of genes that respond to sex-specific selection.
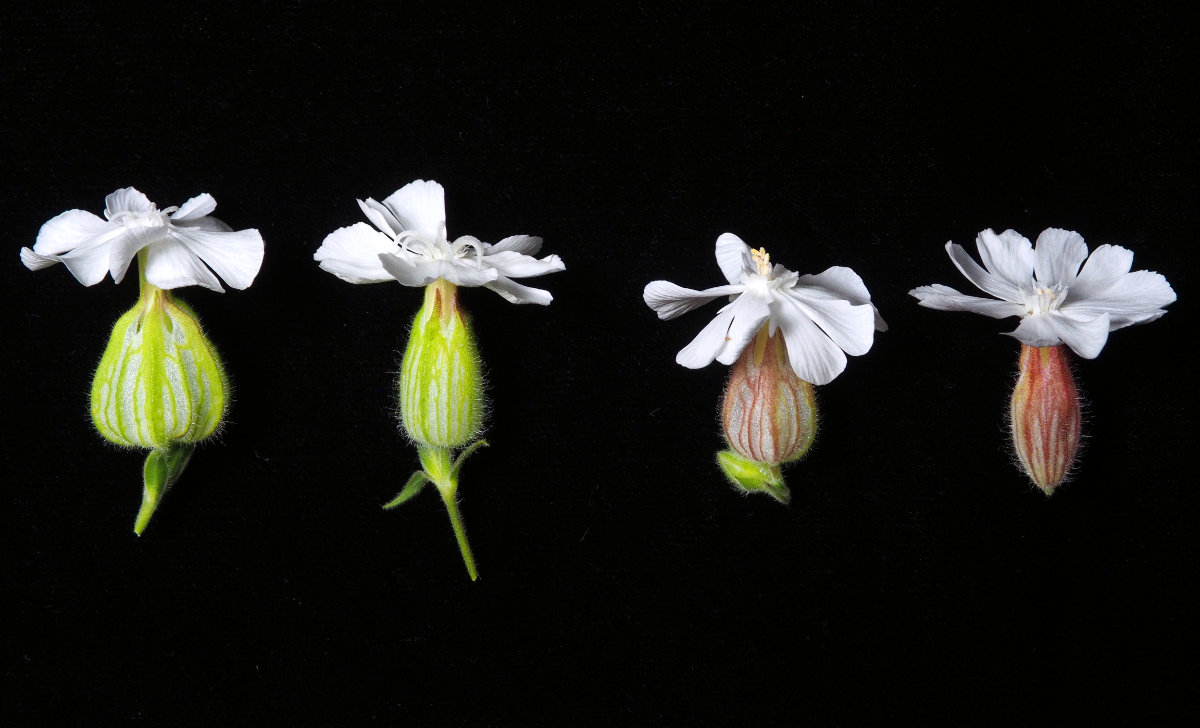

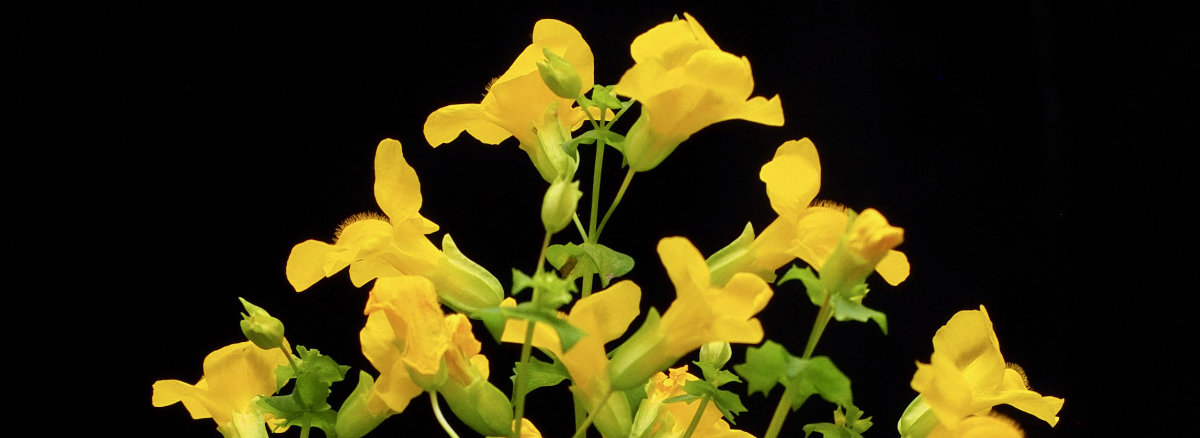
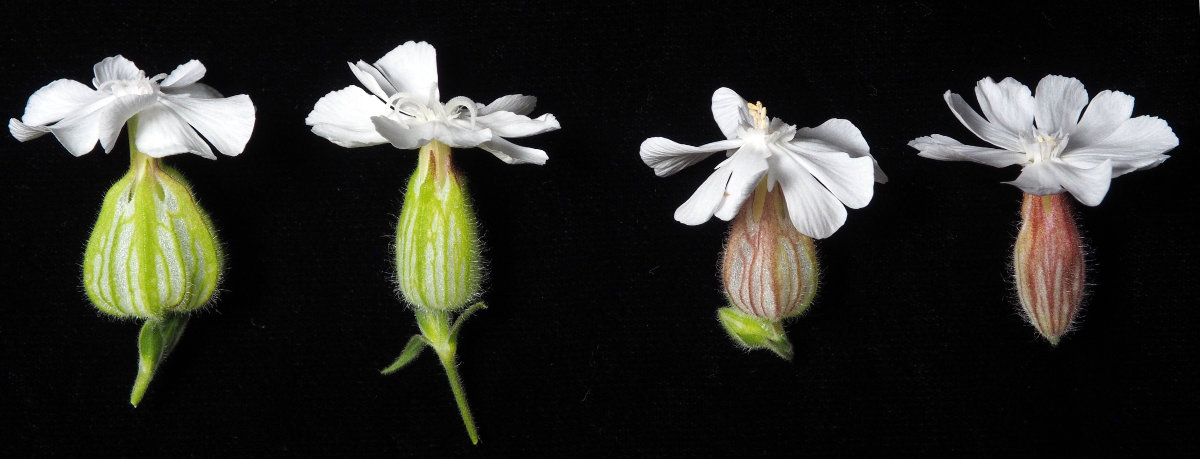
Example female (left) and male (right) flowers from the small and large flower size selection lines.